Networking
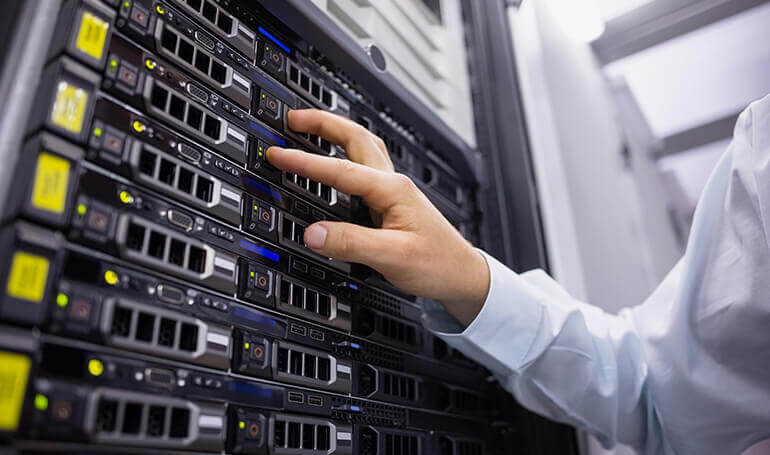
Server
A server is a computer that provides data and services to other computers over a network, such as a LAN or the Internet. Different types of servers exist, including web servers, mail servers, file servers, and database servers, each running specialized software. A database server manages and organizes data, while an application server facilitates communication between applications and databases. Mail servers enable email delivery, and web servers allow users to browse the internet. Other essential servers include FTP servers for file transfers, print servers for managing print jobs, proxy servers for internet access control, and DNS servers for domain name resolution.
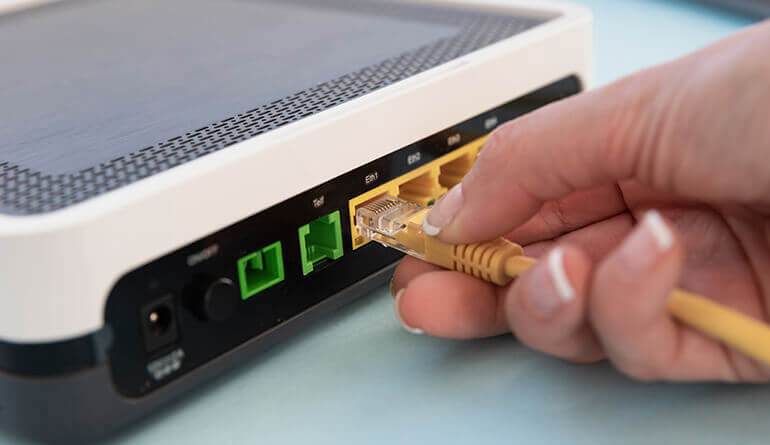


Router
Routing is the process of directing data packets between different networks, such as multiple LANs, ensuring efficient communication across connected devices. Routers play a crucial role in managing network traffic by analyzing the destination of each packet and determining the best path for transmission. They use routing tables and policies to forward data to the appropriate next hop, ensuring smooth and reliable connectivity. Acting as a gateway, a router serves as the network's outermost connection point to external networks, including the Internet. Advanced routing techniques, such as dynamic routing and load balancing, enhance performance and security, optimizing network efficiency.
WIFI Router
WiFi routers make it easy to build a fast, reliable network for your home by enabling wireless connectivity for multiple devices. A wireless router not only directs data traffic but also acts as an access point, transmitting data through radio signals. Modern routers use advanced technologies like MU-MIMO (Multi-User, Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output), which allows them to communicate with multiple devices simultaneously. This reduces latency, decreases wait times, and improves overall network speed. Additionally, features such as dual-band and tri-band support, beamforming, and enhanced security protocols ensure a stable, efficient, and secure internet experience for users.
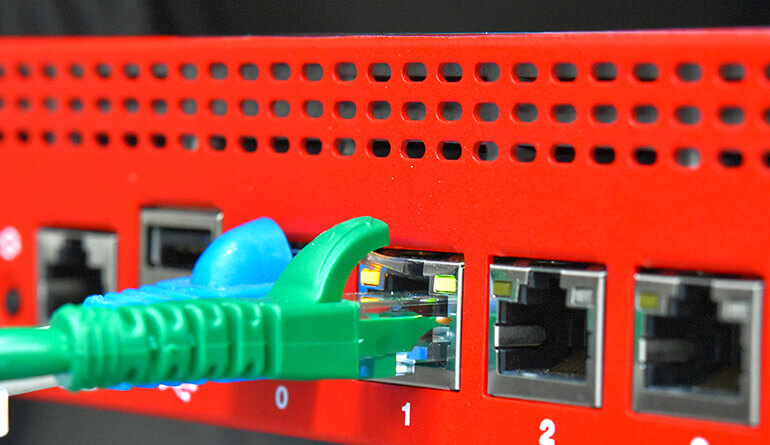


Switch
Switches play a vital role in networking by enabling devices within the same LAN to communicate efficiently. They act as controllers, directing data packets between computers, printers, phones, and other networked devices, enhancing resource sharing and productivity. Businesses rely on switches to create reliable and scalable networks. There are two main types of switches: unmanaged and managed. Unmanaged switches work straight out of the box, requiring no configuration, making them ideal for simple networking needs. Managed switches, on the other hand, offer advanced features, including security controls, remote monitoring, and network optimization, providing greater flexibility and control over the network.
Cables
Network cables serve as the backbone of network infrastructure, enabling communication between devices by transmitting data efficiently. There are three main types of network cables: coaxial, twisted pair, and fiber optic. Coaxial cables consist of a solid copper core surrounded by an insulator, making them resistant to internal and external interference. Twisted pair cables, commonly used in LAN environments, feature pairs of unshielded wires twisted together to minimize signal interference and are easy to install. Fiber optic cables, designed for high-speed data transmission over long distances, use light signals instead of electrical signals, ensuring better security and minimal signal loss.